Although Macs are reliable machines, they are not exempt from hiccups. All you need to do is carry around a single USB flash drive to be ready for situations the require you to diagnose, repair, or experiment with Mac OS X.
You can also click the Launchpad icon on your dock, click the Other folder, and then click Disk Utility. Fast internet browser for windows vista. Or, open a Finder window, click Applications in the sidebar, double-click the Utilities folder, and then double-click Disk Utility. Lightweight, yet reliable boot disk creator that packs additional tools All things considered, Bootdisk Utility is a handy portable application that can help you create bootable disks from your. Open Disk Utility and select View Show All Devices from the menu bar. You should see the device names for each of your drives appear in the sidebar. Alternatively, use the shortcut Cmd + 2. Select the parent folder for the drive you want to reformat or erase, then click the Erase button again. I can successfully use the Startup Disk selection in System Preferences. I'm going to continue to tinker around and attempt to swap the disk numbers if I can. Update: Apple also has written up a support article detailing how to switch in between Windows and Mac OS X. Web browser for windows 10 free download.
One of the maintenance tools every Mac user should have available in case of emergency is a bootable copy of Mac OS X on a removable device. A clean installation of the operating system can help pinpoint problems and will come to the rescue in a bind. And since most Mac owners use a MacBook of some kind nowadays, portability is a valuable thing. That means carrying around a bulky external hard drive with cables is not always ideal. It turns out a tiny USB flash drive serves as a great alternative.
Os X Startup Disk Utility Mac
Not sure when having OS X loaded on a flash drive would come in handy? Here are just a few examples:
- Your Mac isn't starting correctly and you're not sure if the internal hard drive is failing or if another piece of hardware is to blame.
- The file system on your startup disk has become corrupt and needs to be repaired.
- A software problem is plaguing your Mac and you'd like to see if you can replicate it in an isolated environment.
- Your Mac's hard drive is completely dead and you'd like to use your computer for basic tasks like email and web browsing while you wait for your new drive to arrive.
Now that you're convinced, let's figure out how to do this. First you'll need an Intel-based Mac from the past few years. Second, at least a 16GB USB flash drive, such as this SanDisk Cruzer Micro for about $30 at Amazon. Keep in mind 10.6 Snow Leopard was used to demonstrate this tutorial, so I'm not sure how much space 10.5, 10.4, and earlier require. While they should be fine, squeeze those versions of Mac OS X on a 16GB drive at your own risk. And the third thing you'll need to get the job done is your OS X installation DVD.
- To start things off, connect the USB flash drive to your Mac. Make sure there's no valuable data on there because it will be permanently wiped out in a couple minutes.
- Open Disk Utility (Applications > Utilities) and click on your flash drive in the list on the left.
- Go to the Partition tab and select '1 Partition' from the Volume Scheme menu. Enter a name for the volume (I called mine 'OS X USB'), select 'Mac OS Extended (Journaled)' as the Format, and make sure the size is somewhere around 15-16GB.
- Click on the Options button towards the bottom and choose 'GUID Partition Table' from the popup window. Click OK.
- Now that all of the settings have been chosen, click the Apply button and then Partition. Disk Utility will take a minute or two to complete the task.
- I don't believe this step is required, but it makes me feel better and doesn't hurt. Click on the volume name you entered in Step 3 (in the list under the flash drive's name). Go to the Erase tab, make sure the Format is 'Mac OS Extended (Journaled),' and click the Erase button.
- Insert your Mac OS X installation disc if you haven't already. A window should pop up with the contents of the disc. Double-click the 'Install Mac OS X' icon and progress through the installer until you get to the screen that says 'Mac OS X will be install on…'
- Click the Show All Disks button and select your USB flash drive.
- Click on the Customize button and a new window will appear. Un-check all of the items except 'Essential System Software.' You may choose to check 'Rosetta' and 'QuickTime 7' since they are so small and might come in handy. Click OK and then Install. The rest of the process should be automated and might take between 30-60 minutes since USB flash drives are slower than internal hard drives. When all is said and done, you should find about 9GB of your 16GB drive has been filled.
- Eventually, the installation will finish and it should reboot directly to the USB drive. If it doesn't, restart the Mac manually and hold down the Option key to choose the drive yourself. This is how you will access it in the future, too.
- Set up the fresh installation just like you would a new computer. Once you're in, run Software Update a few times to get the latest patches and install any third party diagnostic utilities you may have. For example, Alsoft's DiskWarrior is an invaluable tool that goes above and beyond what OS X's own Disk Utility has to offer. This way both tools are available in one convenient place whenever you need them.
All done! That wasn't too painful, was it? Yes, booting to the flash drive will be a tad sluggish, but it's not meant to be used on a regular basis. This is mainly for diagnosing issues and trying potentially risky things in a virtual sandbox that won't ruin any of your data. While you'll hopefully never need to use it, having a bootable copy of OS X on a USB flash drive is a cost-effective, portable emergency tool for your Mac.
Summary: This post introduces how to boot Mac to Disk Utility and use it, in case you misuse Disk Utility and bring problems like data loss and Mac not booting up. You can also open Disk Utility in macOS Recovery mode to fix some issues.
Many people are looking for good third-party disk management tools. But compared with those paid software, Disk Utility is more reliable as it's built inside the Mac operating system. In addition to normal disk management, it can launch from the Mac recovery boot drive as a recovery tool. This helps a lot when Mac won't start.
Usually, only 3 steps are required to boot to Disk Utility.
- 1. Turn off your Mac.
- 2. Restart your Mac and boot it to macOS Recovery mode.
- 3. Select Disk Utility on the macOS Utilities window.
To get into macOS Recovery Mode:
• How to Boot into & Use M1 Mac Recovery Mode
Before you get more details about booting Mac to Disk Utility, you might need a better understanding of Disk Utility.
About Mac's Disk Utility
Disk Utility is a system utility for performing disk and disk volume-related tasks on macOS and Mac OS X systems. With this easy-to-use program, you can perform tasks as the following:
- Mount, unmount, and eject connected hard drives including SSDs.
- Create, resize, and delete partitions by allocating space of storage devices.
- Erase and format disks with multiple file system options supported.
- Combine multiple hard disks into a RAID set for better performance and reliability with increased storage capacity.
- Create, backup, convert, compress, encrypt, and restore disk images.
- Verify a disk's integrity and repair it with First Aid if the disk is damaged or corrupted.
Some other features are dismissed along with the development of Mac operating systems. For example, you can't repair disk permissions in Disk Utility anymore in macOS. Even so, it's undeniable that what Disk Utility can do now is still good enough in many ways.
Disk Utility brings more insights into disk management on Mac, on condition that you use this tool in the right way.
Problems after a misuse of Disk Utility
Of course, you can perform many disk-related tasks with Disk Utility, simple and easy. But the risk of using Disk Utility is also an important part that you should know. If you don't use Disk Utility in the right way, you could get into trouble. Usually, there are three possible problems.
Mac Os X Disk Utility
1. Data loss after using Disk Utility
Your documents, emails, photos, music, movies, etc. could get lost after your misoperation. If you don't back up the data, you'll lose files after you erased a hard drive, deleted an APFS volume, or formatted a partition.
So, be careful with these options mentioned above and always back files up.
2. Disk corruption
Except for files being deleted, what's worse is that the hard drive itself is corrupted. For example, you should always choose the Eject button before removing an external hard drive. If you don't, the risk of disk corruption is increased. The next time you want to access the external hard drive on Mac, you could receive an error message like 'The disk you inserted was not readable by this computer.'
3. System crashes
The worst case is system crash because you deleted one of the key partitions in the startup disk. For instance, when you add a new partition to the internal SSD, some core partitions could be deleted by the system in rebuilding the partition table.
For Macs whose startup drive is formatted with HFS+, the Mac won't turn on after a wrong deletion of disk0s1 or the EFI boot partition. Similar things happen to APFS formatted boot drive as well, especially for Macs that have the Apple's T2 security chip. If you accidentally removed volumes like Recovery and VM, MacBook or Mac mini introduced after 2018 will have boot problems. It's because the T2 security chip fails to verify the integrity of the boot process.
So, if you see unknown volumes listed under the startup disk, always check through this volume before you finally remove it. Also, you should pay more attention when you want to re-partition the internal hard drive.
How to boot to Disk utility on Mac?
Based on if you can turn on and boot your Mac, there are mainly two ways to access Disk Utility.
1. Open Disk Utility on Mac in a normal startup
It's relatively easy to access Disk Utility after Mac boots up. You can follow these steps to open Disk Utility. You can either find this utility by spotlighting 'disk utility', or you can access it by going to Finder > Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility. Then, you can open Disk Utility and enjoy the features mentioned above.
2. Boot Mac to Disk Utility
Another situation that you want to access Disk Utility is when Mac is not turning on. The symptoms vary from a flashing folder at Mac startup to a frozen loading bar with or without an Apple logo. Then, you need to check if the boot drive is corrupted and fix related issues with Disk Utility.
So, follow this guide to use Disk Utility and boot the problematic Mac again.
- 1. Make sure your Mac has completely turned off. If your Mac is frozen, you can hold the power button until the Mac shuts down.
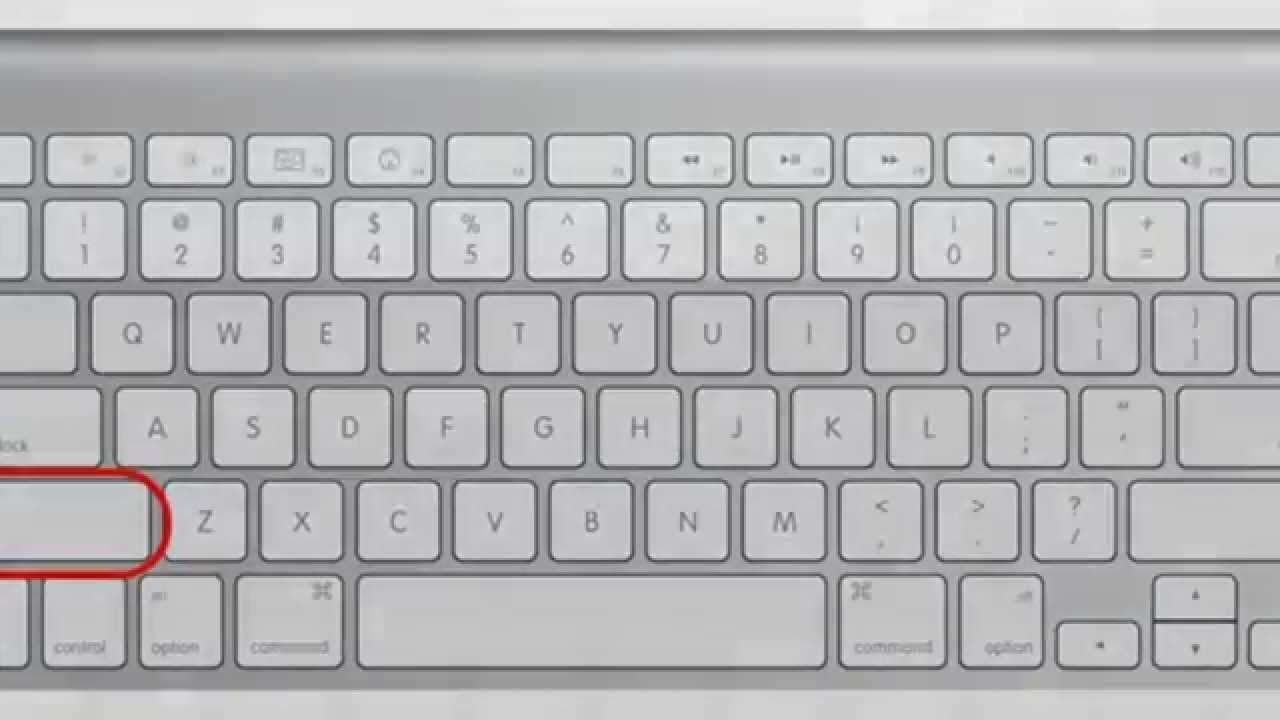
- 2. Restart the Mac and instantly hold Command + R keys to boot Mac into macOS Recovery mode. You can release these keys when you see the Apple logo.
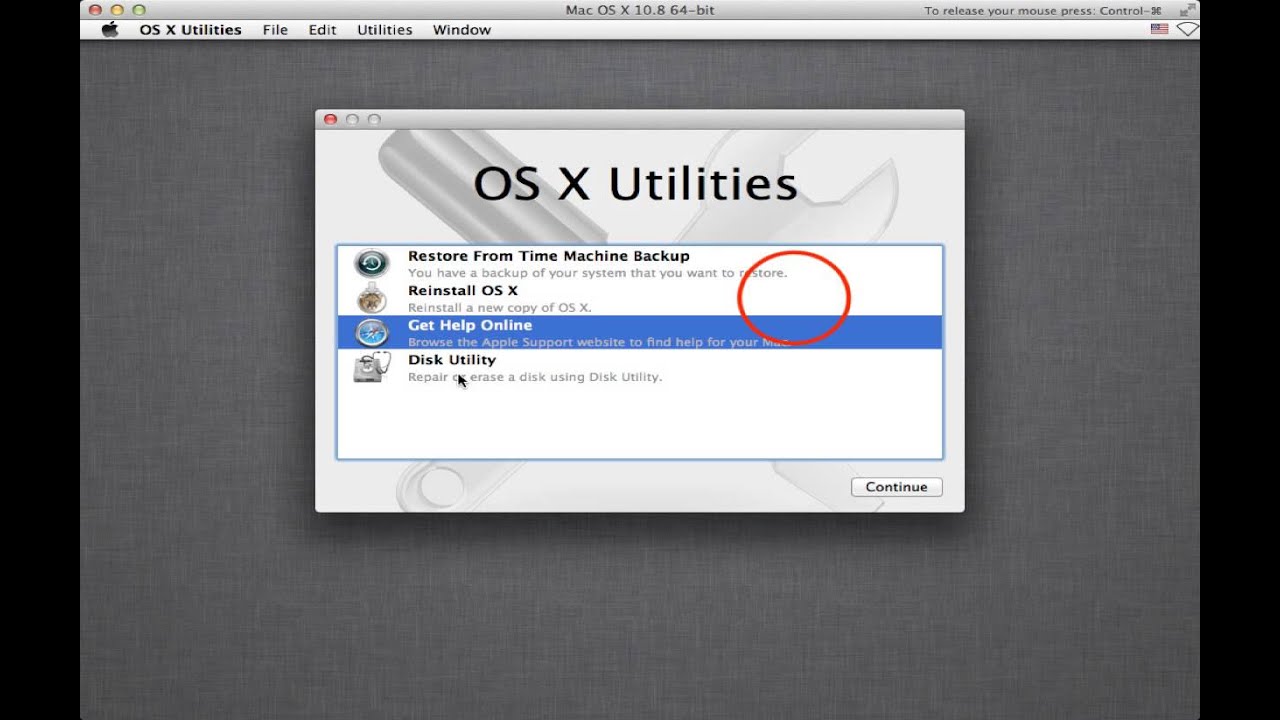
- 3. You'll see a macOS Utilities or Mac OS X Utilities window, which depends on your Mac operating system.
- 4. Select Disk Utility to repair or erase a disk.
If you doubt that there are some errors inside the startup disk, you can use First Aid to repair it. Here is how to do this.
- 1. In Disk Utility Window, select your boot drive and click on First Aid on the top.
- 2. Choose the Run button to confirm that you need to repair this drive.
- 3. After First Aid on the startup drive, your Mac should boot as normal.
If First Aid failed, then the file system of the startup disk might be corrupted. You need to fix it by reformatting the corrupted internal hard drive or SSD, which will replace the problematic file system with an intact one.
Despite this, you should know that reformatting will return you a blank and empty disk. That's to say, you'll lose all your data on the startup disk if you have never backed up your files. Fortunately, Mac data recovery software like iBoysoft Data Recovery for Mac now is available to recover data even when Mac is not turning on.
How to Recover Data in macOS Recovery mode When Mac Won't Boot

3. System crashes
The worst case is system crash because you deleted one of the key partitions in the startup disk. For instance, when you add a new partition to the internal SSD, some core partitions could be deleted by the system in rebuilding the partition table.
For Macs whose startup drive is formatted with HFS+, the Mac won't turn on after a wrong deletion of disk0s1 or the EFI boot partition. Similar things happen to APFS formatted boot drive as well, especially for Macs that have the Apple's T2 security chip. If you accidentally removed volumes like Recovery and VM, MacBook or Mac mini introduced after 2018 will have boot problems. It's because the T2 security chip fails to verify the integrity of the boot process.
So, if you see unknown volumes listed under the startup disk, always check through this volume before you finally remove it. Also, you should pay more attention when you want to re-partition the internal hard drive.
How to boot to Disk utility on Mac?
Based on if you can turn on and boot your Mac, there are mainly two ways to access Disk Utility.
1. Open Disk Utility on Mac in a normal startup
It's relatively easy to access Disk Utility after Mac boots up. You can follow these steps to open Disk Utility. You can either find this utility by spotlighting 'disk utility', or you can access it by going to Finder > Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility. Then, you can open Disk Utility and enjoy the features mentioned above.
2. Boot Mac to Disk Utility
Another situation that you want to access Disk Utility is when Mac is not turning on. The symptoms vary from a flashing folder at Mac startup to a frozen loading bar with or without an Apple logo. Then, you need to check if the boot drive is corrupted and fix related issues with Disk Utility.
So, follow this guide to use Disk Utility and boot the problematic Mac again.
- 1. Make sure your Mac has completely turned off. If your Mac is frozen, you can hold the power button until the Mac shuts down.
- 2. Restart the Mac and instantly hold Command + R keys to boot Mac into macOS Recovery mode. You can release these keys when you see the Apple logo.
- 3. You'll see a macOS Utilities or Mac OS X Utilities window, which depends on your Mac operating system.
- 4. Select Disk Utility to repair or erase a disk.
If you doubt that there are some errors inside the startup disk, you can use First Aid to repair it. Here is how to do this.
- 1. In Disk Utility Window, select your boot drive and click on First Aid on the top.
- 2. Choose the Run button to confirm that you need to repair this drive.
- 3. After First Aid on the startup drive, your Mac should boot as normal.
If First Aid failed, then the file system of the startup disk might be corrupted. You need to fix it by reformatting the corrupted internal hard drive or SSD, which will replace the problematic file system with an intact one.
Despite this, you should know that reformatting will return you a blank and empty disk. That's to say, you'll lose all your data on the startup disk if you have never backed up your files. Fortunately, Mac data recovery software like iBoysoft Data Recovery for Mac now is available to recover data even when Mac is not turning on.
How to Recover Data in macOS Recovery mode When Mac Won't Boot
Here is a guide to recover and rescue files from MacBook Pro, Mac mini, MacBook Air, and iMac when it is not turning on. Read more >>
After you get all files off the crashed Mac, you can continue reformatting the failed startup disk with Disk Utility. Let's get it underway.
- 1. You need to access Disk Utility by booting Mac into macOS Recovery mode as you did before. Do this simply by restarting your Mac and holding Command + R keys right away.
- 2. Find Disk Utility in Mac OS X Utilities (or macOS Utilities) and open it.
- 3. Select the failed Mac hard drive which usually is called Macintosh HD or Apple SSD. Then, click on the Erase button.
- 4. In the pop-up window, name it as Macintosh HD, choose a Format, and select a scheme for the drive.
- 5. Click on Erase to confirm this operation.
After reformatting, Disk Utility has done his job. Then, you can go back to macOS Utilities and choose reinstall macOS or Mac OS X so that you can boot from this drive again.
Sum up
As you can see, Disk Utility does help a lot in managing hard drives and SSDs on Mac. You can even boot to Disk Utility in macOS Recovery mode and fix Mac boot problems, which is impossible for most third-party programs. It also can be accessed in Terminal if you a command-line lover. Now, you can make use of Disk Utility whenever you encounter a disk-related issue.
